Պատկեր:Glacier Mass Balance Map.png
Glacier_Mass_Balance_Map.png (650 × 477 փիքսել, նիշքի չափը՝ 75 ԿԲ, MIME-տեսակը՝ image/png)
Նիշքի պատմություն
Մատնահարեք օրվան/ժամին՝ նիշքի այդ պահին տեսքը դիտելու համար։
| Օր/Ժամ | Մանրապատկեր | Օբյեկտի չափը | Մասնակից | Մեկնաբանություն | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ընթացիկ | 15:56, 2 Հոկտեմբերի 2016 | 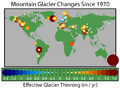 | 650 × 477 (75 ԿԲ) | Cmdrjameson | Compressed with pngout. Reduced by 33kB (30% decrease). |
| 06:48, 10 Ապրիլի 2006 |  | 650 × 477 (108 ԿԲ) | Pflatau | == Summary == The effective rate of change in glacier thickness, also known as the glaciological mass balance, is a measure of the average change in a glacier's thickness after correcting for changes in density associated with the compaction o |
Նիշքի օգտագործում
Հետևյալ էջը հղվում է այս նիշքին՝
Նիշքի համընդհանուր օգտագործում
Հետևյալ այլ վիքիները օգտագործում են այս նիշքը՝
- Օգտագործումը ar.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը cs.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը de.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը en.wikipedia.org կայքում
- User:Dragons flight/Images
- Holocene glacial retreat
- Glacier mass balance
- Retreat of glaciers since 1850
- Talk:Retreat of glaciers since 1850/Archive 2
- Wikipedia:Reference desk/Archives/Science/2006 September 26
- Portal:Climate change/Selected panorama
- Portal:Climate change/Selected panorama/2
- User:Ctello2/sandbox
- Օգտագործումը es.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը eu.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը fi.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը fr.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը gl.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը gu.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը hi.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը hr.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը hu.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը id.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը it.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը ja.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը nl.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը pl.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը ru.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը sh.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը sr.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը sw.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը ta.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը tt.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը vi.wikipedia.org կայքում
- Օգտագործումը zh.wikipedia.org կայքում


